eCommerce Relies on Trust
While your online store may receive a significant amount of traffic, potential customers are often hesitant to provide their credit card and personal information if they don’t trust that your store will protect their data.
Building trust in eCommerce involves implementing best practices for user experience (UX) and website security. This process begins with the development of your website and continues as you manage your store’s operations.
One effective way to build trust and enhance your site’s reputation for all visitors is by implementing an SSL certificate.
In this article, we will explore SSL certificates in detail, including how they function and the six major categories available. By understanding SSL certificates, you can choose the right option to secure your eCommerce store.
Let’s start by discussing what SSL is.
Table of Contents
What is SSL?
SSL, which stands for Secure Sockets Layer, is a cryptographic protocol that adds a layer of security to applications that send or receive data over the Internet.
SSL uses encryption to protect data from being intercepted and read by unauthorized parties. Even if a hacker manages to intercept the data sent to your store, they won’t be able to decipher it due to the strong encryption.
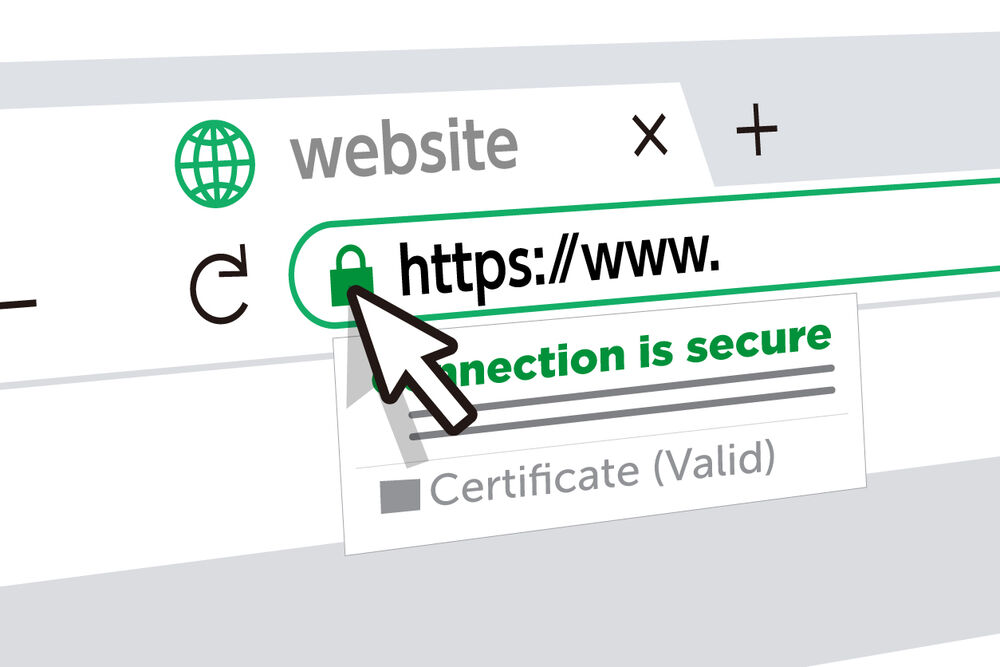
When SSL is activated on a website, users will see a lock icon in their browser’s address bar. This visual indication assures visitors that the website is using SSL to protect their data.
SSL is a crucial security technology that helps protect visitors’ privacy and security, instilling trust in your store’s ability to safeguard user data.
What is an SSL Certificate?
SSL certificates bind a specific cryptographic key to your business’s details, such as the website name, to secure all communications to and from your website.
When an SSL certificate is activated for your store’s domain, the URL changes from HTTP to secured HTTP (HTTPS). Visitors will see a gray padlock icon in the address bar of their browsers, indicating a secure connection.
In addition to the security benefits, search engines incentivize website owners to install SSL certificates by improving their search engine results page (SERP) positions.
Benefits of SSL Certificates for Your Store
Here are five benefits of having SSL certificates for your eCommerce store:
How Do SSL Certificates Work?
SSL certificates employ a combination of private and public keys to secure your store. They validate the secure connection between your store’s website and a web server using public key cryptography.
SSL certificates function in the following manner:
Types of SSL Certificates
SSL certificates are generated and issued by Certificate Authorities (CAs) as bundles that include root and intermediate certificates.
Here are the six major categories of SSL certificates:
Conclusion
Selecting the right SSL certificate for your eCommerce store depends on your specific needs and requirements. Understanding the various types of SSL certificates available enables you to make an informed decision to protect your website and provide a secure browsing experience for your users.
Remember, investing in the appropriate SSL certificate is an investment in your online presence’s trustworthiness and credibility.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: When should I consider requesting a Wildcard SSL Certificate? A: A Wildcard SSL Certificate should be considered when securing multiple subdomains, such as secure.domainname.com, www.domainname.com, and mail.domainname.com. The common name for a Wildcard SSL Certificate is usually in the format “*.domainname.com.”
Q: How do I choose the right type of SSL certificate? A: The right SSL certificate depends on your website’s specific needs, including the level of validation and trust required, the number of subdomains or domains to secure, and your budget. Choosing a reputable Certificate Authority (CA) and ensuring compatibility with different browsers and devices are also important factors to consider.
Q: How long is an SSL certificate valid? A: SSL certificates are typically valid for 1 to 2 years, although some CAs offer longer-term options. It’s crucial to keep track of the certificate’s expiration date and renew it on time to maintain your website’s security.
Q: Can I use a free SSL certificate on my site? A: Free SSL certificate options, such as Let’s Encrypt, are suitable for personal and hobby projects. They offer basic encryption capabilities, particularly for personal websites or blogs. However, if your website handles sensitive data or requires higher trust and validation, it is generally recommended to invest in a paid SSL certificate from a reputable CA.
51 Comments
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-
